The digital world is undergoing a profound transformation. As more critical services—banking, healthcare, government portals, travel, and commerce—move online, the question of how to secure these services has become one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Traditional defenses like passwords and one-time codes are proving increasingly fragile in the face of sophisticated cyberattacks. In response, organizations are embracing a new paradigm: combining artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and biometric authentication to create security systems that are not just stronger, but smarter.
At the core of this shift is a simple principle: digital identity must move beyond what you know (passwords, PINs) and what you have (tokens, devices) to what you are and how you behave. Biometrics such as fingerprints, facial scans, or voice recognition provide a uniquely personal layer of security. However, biometrics alone are not enough. AI and ML bring adaptability—systems that continuously learn, detect anomalies, and evolve as threats change. Together, they create a dynamic defense that is extremely difficult to bypass.
Why Biometrics Alone Isn’t Enough
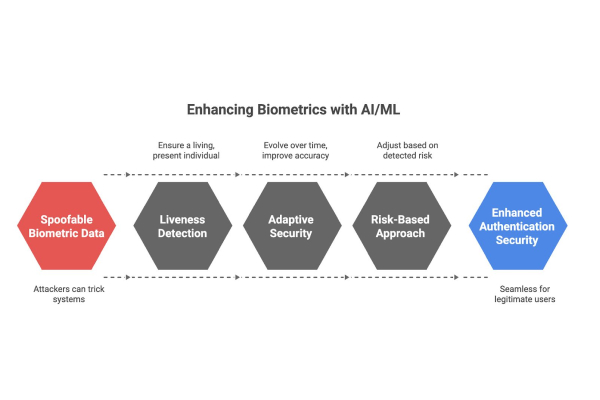
Biometrics have long been celebrated as a breakthrough in authentication. Unlike passwords, they cannot be forgotten, and unlike security tokens, they cannot be misplaced. Yet, biometric data can be spoofed. Photos, deepfakes, or synthetic voice samples have shown that determined attackers can sometimes trick systems into granting access. That is where AI and ML play a pivotal role.
By analyzing subtle cues—such as the texture of a fingerprint, the movement of a live face, or micro-patterns in speech—AI-driven systems can distinguish between a real user and a fraudulent attempt. This is called liveness detection, and it ensures that authentication is tied to a living, present individual rather than a static image or recording. These innovations represent some of the Best Futuristic Features in digital security, as they combine human uniqueness with machine intelligence to outpace cyber threats.
Adaptive Security Through Machine Learning
Where AI and ML truly shine is in their ability to adapt. Traditional rule-based systems are rigid: they block or allow based on pre-set conditions. Machine learning models, however, evolve over time, learning from millions of data points to improve accuracy and reduce false positives.
For example, ML can monitor behavioral patterns—such as typing speed, device tilt, or login times—and use them as secondary signals of authenticity. If a user typically logs in from one region and suddenly appears in another, the system can flag the session for additional verification. The result is a layered approach to security: fast and seamless for legitimate users, but increasingly difficult for attackers to breach.
Balancing Security and User Experience
Security solutions often face a trade-off: stronger defenses can mean more friction for users. The true promise of AI and biometrics lies in striking a balance between the two. Instead of forcing every login to go through multiple steps, intelligent systems adjust based on risk.
If the system detects a low-risk interaction—for instance, a login from a known popular mobile device in a familiar location—the user may pass through seamlessly. But if risk factors are detected—such as access from a new device, an unusual purchase, or atypical behavior—then additional biometric checks are triggered. This risk-based approach ensures that legitimate users experience minimal friction, while attackers encounter ever-higher barriers.
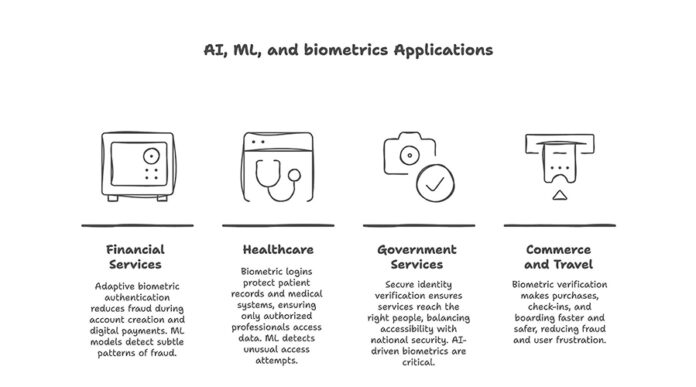
Applications Across Industries
The applications of AI, ML, and biometrics are vast and rapidly expanding.
- Financial Services: Banks and fintech firms use adaptive biometric authentication to reduce fraud during account creation, digital payments, and high-value transactions. ML models can detect subtle patterns of fraud long before humans recognize them.
- Healthcare: Patient records and medical systems are protected with biometric logins that ensure only authorized professionals can access sensitive data. ML adds another layer by detecting unusual access attempts that may signal insider threats.
- Government and Public Services: From tax filing to border control, secure identity verification ensures services reach the right people. AI-driven biometrics are critical to balancing accessibility with national security.
- Commerce and Travel: Retailers and airlines are integrating biometric verification to make purchases, check-ins, and boarding faster and safer, reducing both fraud and user frustration.
Also see: Protect Mobile Phone from Cyber Attack
The Road Ahead
While the potential is enormous, the path forward requires caution and responsibility. Biometrics, once compromised, cannot be reset like a password. That makes data security and privacy protections essential. AI models must also be trained responsibly, avoiding biases that could exclude or misidentify certain demographic groups. Transparency in how these systems operate will be vital to building trust among users.
Despite these challenges, the trajectory is clear. The future of digital security will be built on systems that know who we are and how we behave, not just what we remember. AI and ML will be the engines that keep these systems adaptive, resilient, and responsive to evolving threats. Biometrics will provide the human anchor, ensuring security is personal, unique, and seamless.
In a world where every interaction is digitized, securing valuable services is no longer optional—it is foundational. By combining the intelligence of machines with the uniqueness of human identity, we are creating a future where digital trust is not fragile, but enduring.
Author Bio: Pavan Prasanna Kumar is a Senior Product Manager at AWS. He is passionate about helping customers solve their business challenges through artificial intelligence. In his spare time, he enjoys playing squash, listening to business podcasts, and exploring new cafes and restaurants.